Remote Repo
Generate SSH private and public key
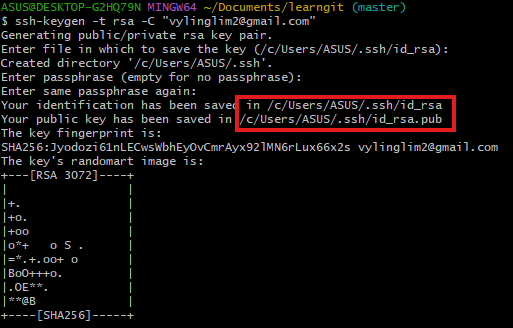
Open Shell (open Git Bash in Windows) and create an SSH Key:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "youremail@example.com"
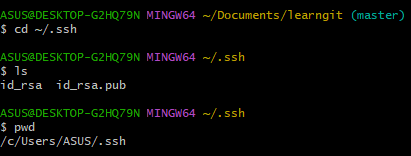
User's home directory .ssh, which contains id_rsa and id_rsa.pub files. These two are the SSH Key key pair.
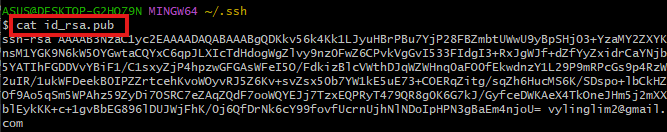
id_rsaare private keys and cannot be leaked.id_rsa.pubare public keys and can be told to anyone with confidence.- copy paste
id_rsa.pubinto youe Github acc
Git repository work with both HTTPS and SSH protocols
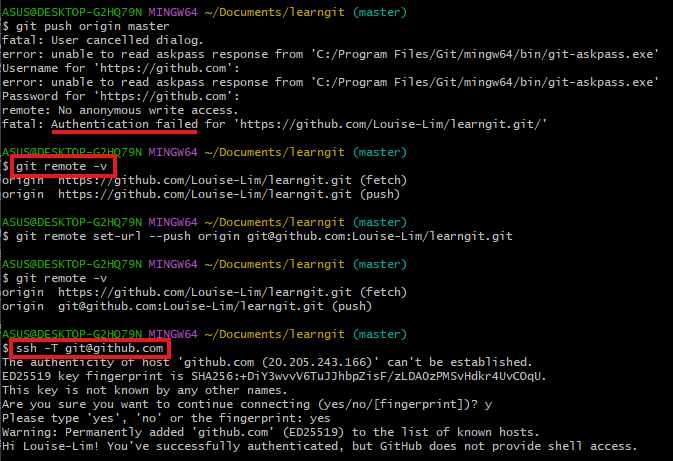
Check your current remote URL with : git remote -v
- If the URL starts with https://github.com, Git will prompt for your GitHub credentials instead of using SSH.
Change the remote URL to use SSH : git remote set-url origin git@github.com:username/repo.git
Verify SSH authentication works : ssh -T git@github.com
Why does GitHub need an SSH Key?
Because GitHub needs to identify that the commits you push are indeed pushed by you, not someone else pretending to be you. Git supports the SSH protocol, so as long as GitHub knows your public key, it can confirm that only you can push.
1.Adding a remote repo
git remote add origin git@github.com:michaelliao/learngit.git
git push -u origin master
Summary
- To associate a remote library, use the command git remote add origin git@server-name:path/repo-name.git;
- When you associate a remote library, you must specify a name for the remote library, originwhich is the default customary naming;
- After associating, use the command to push all the contents of the branch git push -u origin masterfor the first time ;master
- After that, after each local commit, you can use the command to push the latest changes whenever necessary git push origin master;
- One of the biggest benefits of a distributed version control system is that you don't need to consider the existence of a remote repository when working locally, that is, it can work normally whether you have an Internet connection or not, while SVN refuses to work when there is no Internet connection! When there is a network, you can push the local commits to complete the synchronization, which is really convenient!
2. Cloning from a remote repo
git clone <https>